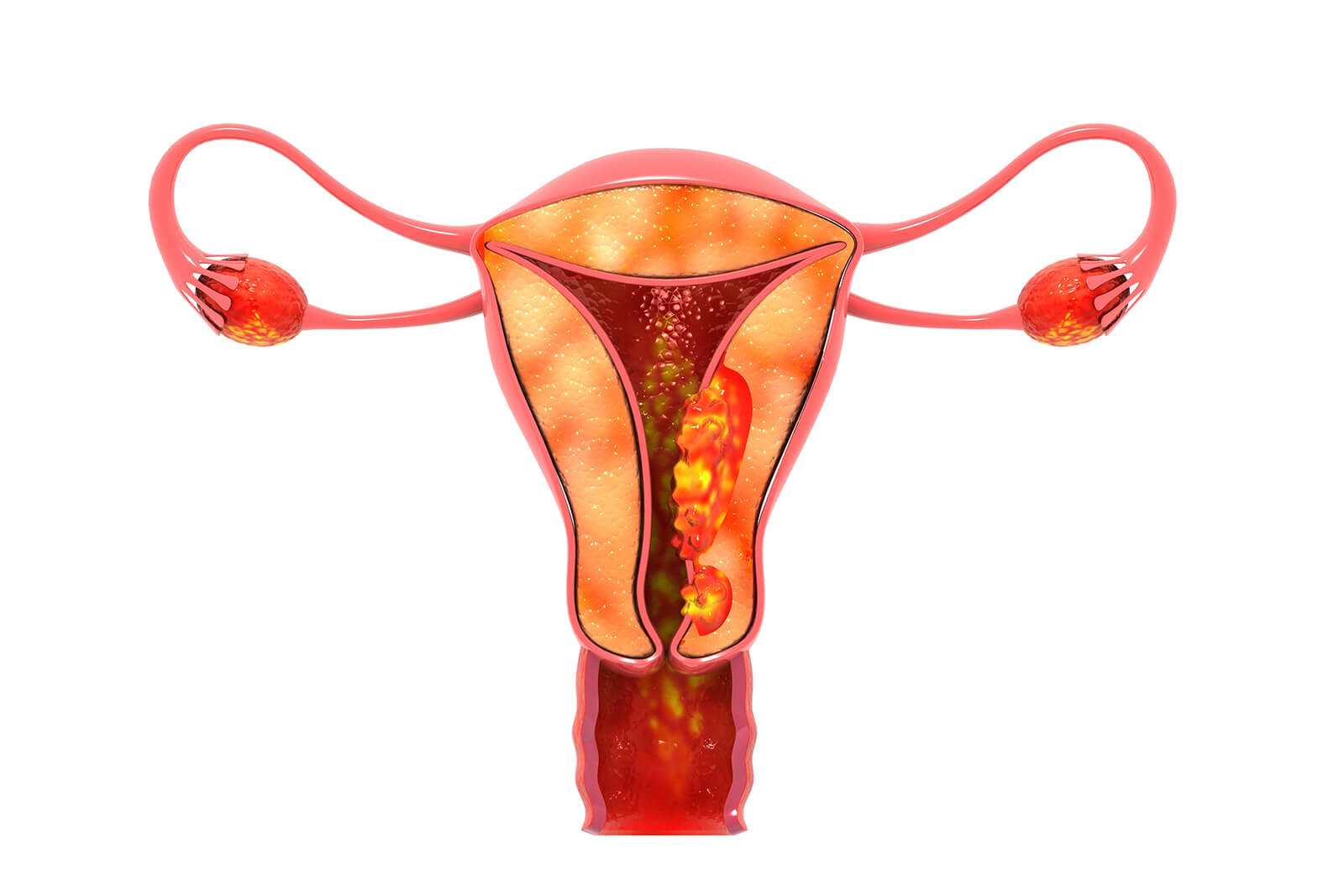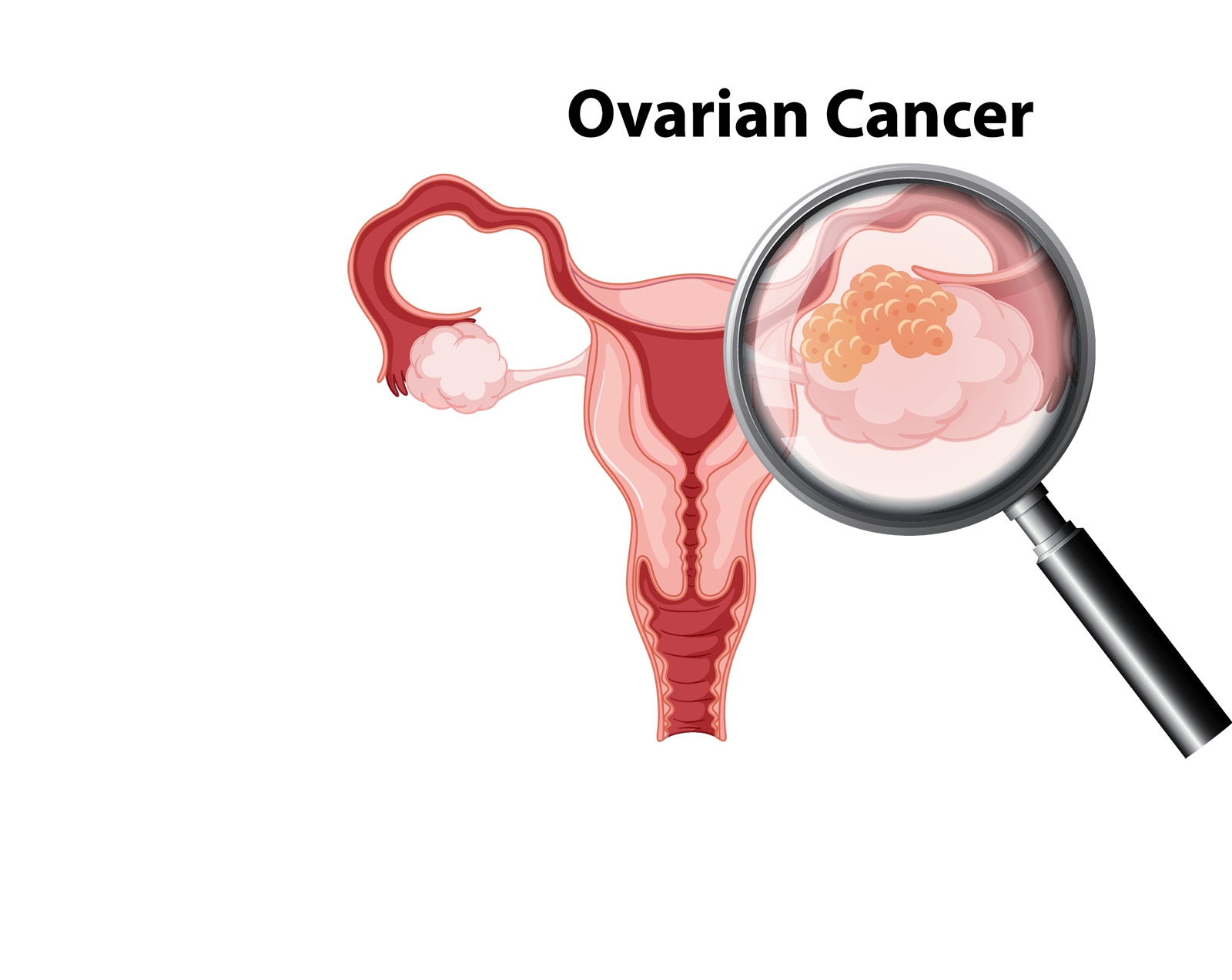
Ovarian cancer is a growth of cells that forms in the ovaries. The cells multiply quickly and can invade and destroy healthy body tissue.
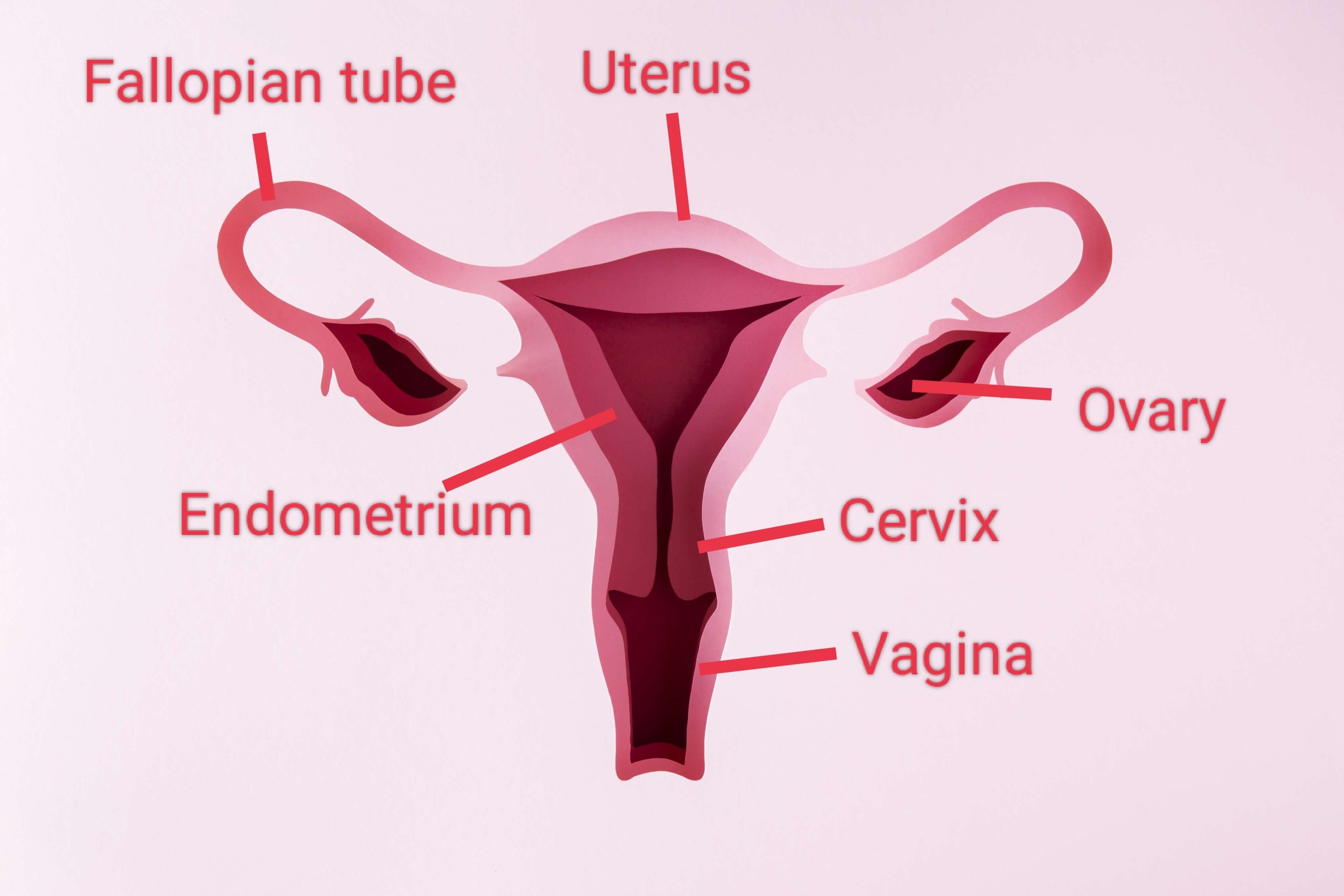
The female reproductive system contains two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries — each about the size of an almond — produce eggs (ova) as well as the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Ovarian tumours can be cancerous or non-cancerous .
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
- Nonspecific complaints like abdominal fullness, bloating.
- Mass in the abdomen
- Difficulty in breathing and performing routine activities
- Menstrual irregularities.
EVALUATION
Based on clinical check up your oncologist will recommend investigations such as CT scan and blood tests (CA-125 and CEA).
HOW IS OVARIAN CANCER TREATED?
Ovarian cancer is most commonly diagnosed in locally advanced form due to its non-specific symptoms. The treatment is tailored based on the stage of the disease which includes chemotherapy and surgery.
Surgical treatment includes staging laparotomy in which uterus, ovaries, regional lymph nodes, omentum and involved organs are removed.